Have you ever felt a sharp pain in your hip while playing sports or even just getting out of bed? You might be experiencing a hip strain or sprain. While these injuries may sound similar, they affect different tissues and require different approaches to treatment.
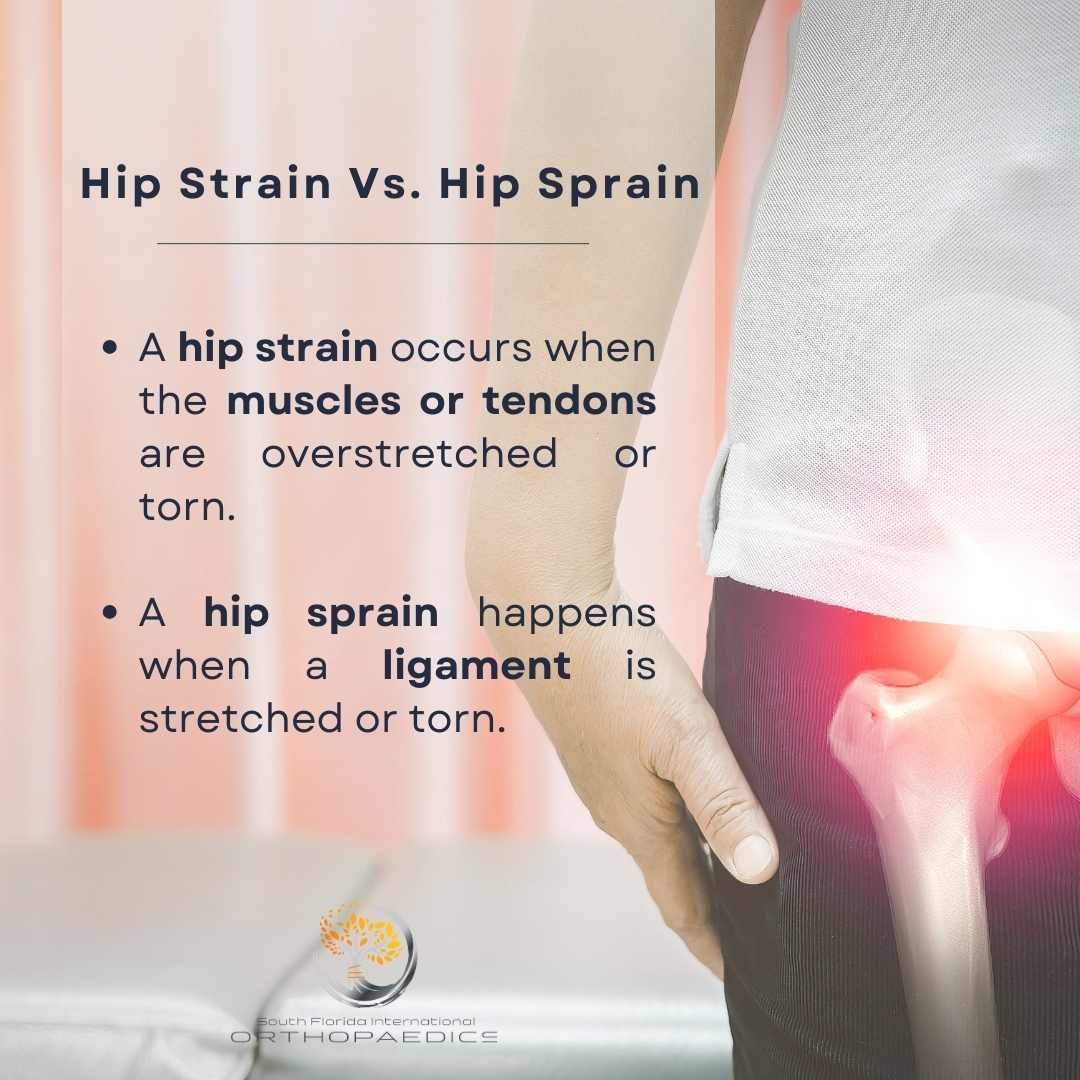
Understanding the distinction between a hip strain and a hip sprain is crucial for effective recovery.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the differences between these two common injuries, their symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
Hip strain vs. hip sprain: What’s the difference?
A hip strain and a hip sprain are both painful injuries, but they occur in different parts of the hip joint. To understand the difference, let’s break down the anatomy.
- Muscles and tendons: Muscles are the tissues responsible for movement, while tendons connect muscles to bones. A hip strain occurs when these muscles or tendons are overstretched or torn.
- Ligaments: Ligaments are tough, fibrous tissues that connect bones to bones, providing stability to the joint. A hip sprain happens when a ligament is stretched or torn.
Hip strains are more common than hip sprains. This is because the hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint, offering a wide range of motion, which increases the likelihood of muscle strain. However, severe trauma, such as a car accident or a fall, can result in a hip sprain.
What causes hip strain and sprain?
Hip strains and sprains are often caused by:
- Overuse: Repetitive movements, especially in sports or physically demanding jobs, can strain the muscles and ligaments in the hip.
- Trauma: A direct blow to the hip, such as from a fall or a collision, can cause a sprain.
- Sudden movements: Twisting or turning the hip abruptly can overstretch the muscles or ligaments.
- Insufficient warm-up: Not properly warming up before physical activity can increase the risk of injury.
- Muscle weakness or imbalance: Weak hip muscles can make the joint more susceptible to injury.

What are the symptoms of a hip strain and sprain?
Recognizing the symptoms of a hip strain or sprain is essential to determine the right course of action. While there can be an overlap in symptoms, some key differences can help you identify the type of injury.
Hip strain symptoms
- Pain in the hip, groin, or thigh
- Muscle tenderness and stiffness
- Swelling and bruising
- Decreased range of motion
- Weakness in the hip muscles
Hip sprain symptoms
- Intense pain in the hip joint
- Joint instability
- Swelling and bruising
- Difficulty bearing weight
Remember, these are general symptoms. The severity of the pain and other symptoms may vary depending on the extent of the injury.
If you experience severe pain, difficulty walking, or any signs of instability, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly.
How are hip strains and sprains treated?
Most symptoms of hip strains and sprains get better with conservative treatment options, such as the following:
RICE Method
The RICE method is a common first-aid treatment for many soft tissue injuries, including hip strains and sprains.
- Rest: Avoid activities that cause pain. This allows the injured area to heal.
- Ice: Applying ice packs to the injured area for 15-20 minutes every few hours can help reduce swelling and pain. Wrap the ice pack in a thin cloth to protect your skin.
- Compression: Wrapping the injured area with an elastic bandage can help reduce swelling. However, it should not be too tight, as it can restrict blood flow.
- Elevation: Raising the injured hip above your heart whenever possible can help reduce swelling.
Physical therapy
Physical therapy is often recommended for hip strains and sprains that don’t improve with home treatment or for more severe injuries. A physical therapist can:
- Teach you specific exercises to strengthen the muscles around your hip.
- Improve flexibility and range of motion.
- Reduce pain and inflammation.
- Help you return to your normal activities safely.
Medications
Over-the-counter medications can help manage pain and inflammation associated with hip strains and sprains. Common options include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These medications, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, can reduce pain and inflammation.
- Acetaminophen: While it helps with pain, it doesn’t reduce inflammation. It can be a good option if you can’t take NSAIDs.
Always follow the directions on the medication label and consult your doctor if you have any concerns or if the pain doesn’t improve.
When is surgery recommended?
Surgery is typically not the first line of treatment for hip strains and sprains. Most cases respond well to non-surgical methods such as those listed above. However, in rare and severe cases, surgery might be considered. This is often when:
- A tendon is completely torn: If a tendon is completely detached from the bone, surgery might be necessary to reattach it.
- Chronic instability: If the hip joint remains unstable despite non-surgical treatments, surgical stabilization might be an option.
- Failed conservative treatment: If other treatment methods haven’t improved the condition after a significant period, surgery could be explored.
It’s crucial to emphasize that the decision to undergo surgery should be made in close consultation with an orthopedic surgeon. They will carefully evaluate the specific circumstances of your injury and recommend the best course of action.
When can you return to normal activities?
The timeframe for returning to normal activities after a hip strain or sprain varies depending on the severity of the injury.
- Mild strains: You might be able to return to normal activities within a few weeks with proper home care.
- Severe strains: Recovery can take several months, and in some cases, surgical repair and extensive physical therapy may be necessary.
It’s crucial to gradually increase your activity level to avoid re-injury. Start with low-impact activities and progressively increase the intensity as your hip strength and flexibility improve.
Always consult with your orthopedic doctor or physical therapist before returning to your regular activities.
How do you prevent hip strains and sprains?
Preventing hip strains and sprains involves a combination of factors:
- Warm-up: Always warm up before any physical activity. This increases blood flow to the muscles and prepares them for exertion.
- Stretching: Incorporate stretching into your routine to improve flexibility and reduce the risk of muscle strains.
- Strengthening exercises: Building strength in the hip muscles can enhance stability and reduce the likelihood of injuries.
- Proper footwear: Wearing appropriate shoes for your activities can provide support and reduce stress on the hip joint.
- Cross-training: Varying your workouts can help prevent overuse injuries.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight can put additional strain on the hip joint, increasing the risk of injuries.
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to any signs of pain or discomfort and rest when needed.
By following these guidelines, you can significantly reduce your risk of experiencing a hip strain or sprain.
Experience Unmatched Orthopedic Care at South Florida International Orthopaedics
South Florida International Orthopaedics is your premier destination for world-class orthopedic care. Our board-certified orthopedic specialists are at the forefront of medical advancements, offering innovative treatments and personalized care.
Our team at South Florida orthoepdics provide a wide range of orthopedic treatment services and programs, such as:
- Miami sports medicine
- Hip arthroscopy in Miami
- Hip labral tear treatment in Miami
- Hip impingement surgery in Miami
Whether you’re an athlete seeking to return to the field or an individual looking to manage chronic pain, we’re here to help you regain your mobility and independence. Our focus is on restoring your quality of life and getting you back to doing what you love.
Contact us today to request an appointment with our orthopedic doctors.

The material contained on this site is for informational purposes only and DOES NOT CONSTITUTE THE PROVIDING OF MEDICAL ADVICE, and is not intended to be a substitute for independent professional medical judgment, advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified healthcare providers with any questions or concerns you may have regarding your health.
